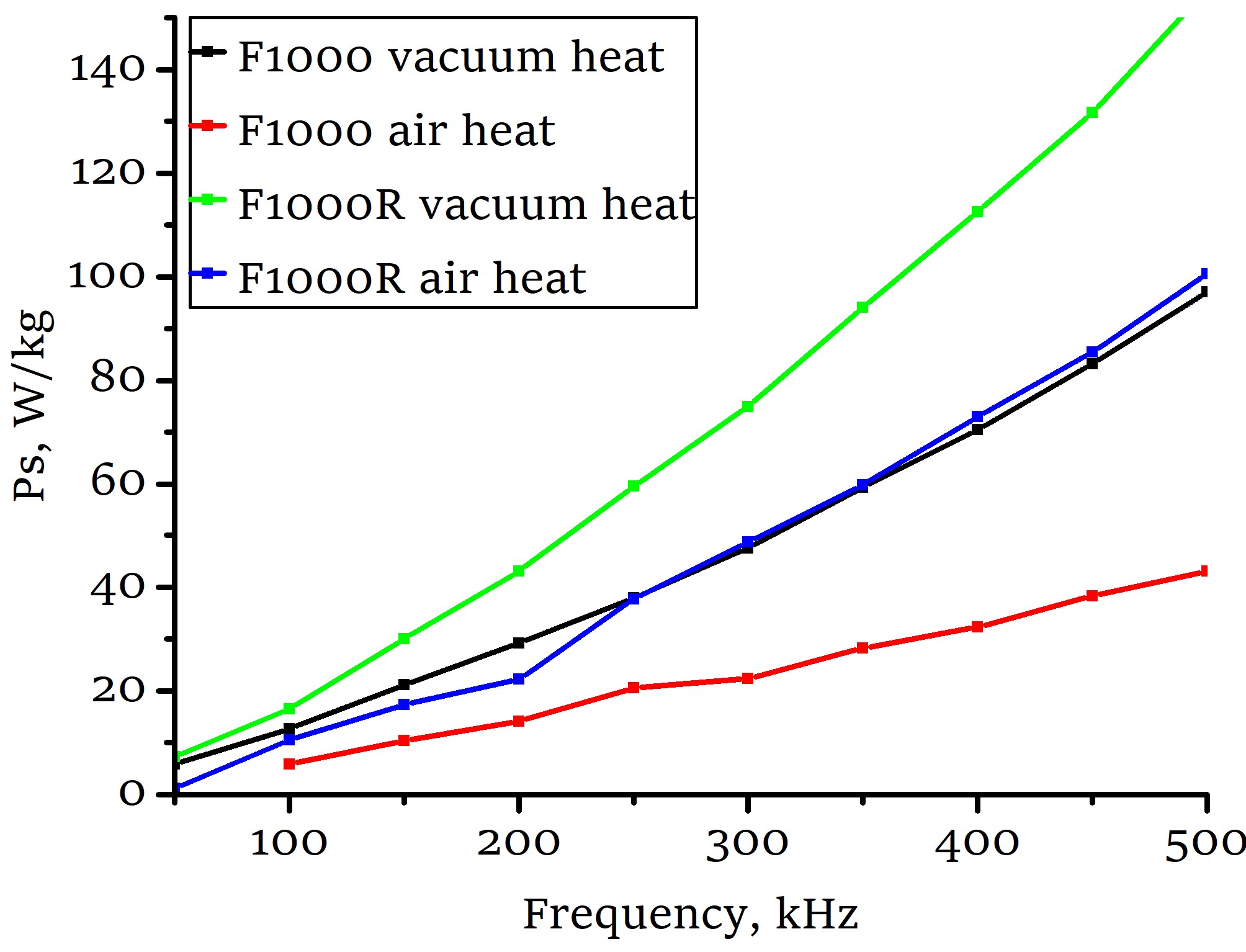
Influence of the powders phase composition and sintering atmosphere on the structure and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrites
Abstract
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Zheng ZG, Zhong XC. Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline ZnxMn1–xFe2O4 prepared by ball milling. J Alloys Compd. 2008;466(1–2):377–382. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.11.112
Guu YH, Tsai KL, Chen LK. An experimental study on elec-trical discharge machining of manganese-zinc ferrite magnetic material. Mater Manuf Process. 2007;22(1):66–70. doi:10.1080/10426910601015949
Sun K, Lan K, Yu Z, Xu Z, Jiang X, Wang Z, Liu Z, Luo M. Temperature and frequency characteristics of low-loss Mn-Zn ferrite in a wide temperature range. J Appl Phys. 2011;109(10):88–91. doi:10.1063/1.3583551
Thakur P, Chahar D, Taneja S, Bhalla N, Thakur A. A review on Mn-Zn ferrites: Synthesis, characterization and applica-tions. Ceram Int. 2020;46(10):15740–15763. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.287
Ji X, Shen C, Zhao Y, Zheng H, Wu Q, Zhang Q, Zheng L, Zheng P, Zhang Y. Enhanced electromagnetic properties of low-temperature sintered NiCuZn ferrites by doping with Bi2O3. Ceram Int. 2022;48(14):20315–20323. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.03.313
Suryanarayana B, Ramanjaneyulu K, Raghavendra V, Mura-li N, Parajuli D, Mulushoa SY, Choppara P, Rao PA, Ramakrishna Y, Chandramouli K. Effect of Sm3+ substitution on dc electrical resistivity and magnetic properties of Ni–Co ferrites. J Indian Chem Soc. 2022;99(8):100623. doi:10.1016/j.jics.2022.100623
Mammo TW, Murali N, Sileshi YM, Arunamani T. Effect of Ce-substitution on structural, morphological, magnetic and DC electrical resistivity of Co-ferrite materials. Phys B Condensed Matter. 2018;531:164–170. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2017.12.049
Han YH, Suh JJ, Shin MS, Han SK. The effect of sintering conditions on the power loss characteristics of Mn-Zn ferrites for high frequency applications. J Phys. 1997;7(C1):111–112. doi:10.1051/jp4:1997133
Zhou Y, Yang G, Yang Y, Qin Y, Yin D, Zhang Y. Effect of heating rate on densification and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrites sintered by multiphysical fields coupling methodology. Adv Appl Ceram. 2014;113(5):257–261. doi:10.1179/1743676113Y.0000000135
Goldman A. Modern Ferrite Technology. Springer Science & Business Media; 2006. 438 p.
Abbas T, Khan Y, Ahmad M, Anwar S. X-ray diffraction study of the cation distribution in the Mn-Zn-ferrites. Solid State Commun. 1992;82(9):701–703. doi:10.1016/0038-1098(92)90064-G
Morineau R, Paulus M. Chart of PO2 versus temperature and oxidation degree for Mn-Zn ferrites in the composition range: 50
Tanaka T. Equilibrium oxygen pressures of Mn‐Zn ferrites. J Am Ceram Soc. 1981;64(7):419–421. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1981.tb09882.x
Žnidaršič A, Drofenik M. Influence of oxygen partial pressure during sintering on the power loss of Mn-Zn ferrites. IEEE Trans Magn. 1996;32(3):1941–1945. doi:10.1109/20.492890
Rahaman MN. Ceramic processing and sintering. CRC Press: New York; 2003. 875 p.
Shijie C, Science M. Effects of heating processing on micro-structure and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrites prepared via chemical Co-precipitation. J Wuhan Univ Tech-nol. 2014;30(4):684–688. doi:10.1007/s11595-015-1212-8
Chien YT, Ko YC. Dependence of magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrites on the degree of calcination. J Mater Sci. 1991;26:5859–5864. doi:10.1007/BF01130125
Song KH, Park JH. Combined effect of partial calcination and sintering condition on low loss Mn-Zn ferrite. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 1999;10:307–312. doi:10.1023/A:1008928903133
Matsuo Y, Ono K, Hashimoto T, Nakao F. Magnetic properties and mechanical strength of MnZn ferrite. IEEE Trans Magn. 2001;37(4):2369–2372. doi:10.1109/20.951175
Liu D, Chen X, Ying Y, Zhang L, Li W, Jiang L, Che S. Mn-Zn power ferrite with high Bs and low core loss. Ceram Int. 2016;42(7):9152–9156. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.03.005
Tsakaloudi V, Kogias G, Zaspalis VT. Process and material parameters towards the design of fast firing cycles for high permeability Mn-Zn ferrites. J Alloys Compd. 2014;588:222–227. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.047
Topfer J, Gablenz S. Effect of oxygen partial pressure control during sintering on the power loss in Mn-Zn ferrites. In: Proc. 9 Th Int. Conf. Ferrites (ICF 9). 2005;3:257–262.
Morineau R, Paulus M. Oxygen partial pressures of Mn-Zn ferrites. Phys Status Solidi. 1973;20(1):373–380. doi:10.1002/pssa.2210200139
Ahns SJ, Yoon CS, Yoon SG, Kim CK, Byun TY, Hong KS. Do-main structure of polycrystalline Mn-Zn ferrites. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol. 2001;84(3):146–154. doi:10.1016/S0921-5107(00)00585-7
Byeon SC, Hong KS, Park JG, Kang WN. Origin of the increase in resistivity of manganese-zinc ferrite polycrystals with oxygen partial pressure. J Appl Phys. 1997;81(12):7835–7841. doi:10.1063/1.365393
Zlatkov BS, Mitrović NS, Nikolić M.V, Maričić AM, Dan-ninger H, Aleksić OS, Halwax E. Properties of Mn-Zn ferrites prepared by powder injection molding technology. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol. 2010;175(3):217–222. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2010.07.031
Sankarshana Murthy MN, Deshpande CE, Shrotri JJ. Preparation of manganous zinc ferrites. Proc Indian Acad Sci Sect A Chem Sci. 1978;87:49–54. doi:10.1007/BF03182115
Michalk C. Mössbauer study of Mn-Zn ferrite formation under low oxygen pressure conditions. J Magn Magn Mater. 1987;68(2):157–159. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(87)90269-1
Wang FFY, Krishnan KM, Cox DE, Reynolds TG. Compositional and structural studies of a Mn-Zn ferrite under different processing conditions. J Appl Phys. 1981;52(3):2436–2438. doi:10.1063/1.328959
Urek S, Drofenik M. Influence of iron oxide reactivity on microstructure development in Mn-Zn ferrites. J Mater Sci. 1996;31:4801–4805. doi:10.1007/BF00355864
Lin WH, Hwang CS. Characteristics of powder and sintered bodies of hydrothermally synthesized Mn-Zn ferrites. J Mater Sci. 2002;37(5):1067–1075. doi:10.1023/A:1014376620601
Stergiou CA, Zaspalis V. The role of prefiring in the devel-opment of Mn-Zn spinel ferrites for inductive power trans-fer. Ceram Int. 2015;41(3):4798–4804. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.12.034
Tsakaloudi V, Zaspalis V. Synthesis of a low loss Mn-Zn ferrite for power applications. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;400:307–310. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.07.064
Yan MF, Johnson DW. Impurity‐induced exaggerated grain growth in Mn‐Zn Ferrites. J Am Ceram Soc. 1978;61(7–8):342–349. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1978.tb09325.x
Sainamthip P, Amarakoon VRW. Role of zinc volatilization on the microstructure development of manganese zinc ferrites. J Am Ceram Soc. 1988;71(8):644–648. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1988.tb06382.x
Suh JJ, Han YH. Quantitative analysis of zinc vaporization from manganese zinc ferrites. J Am Ceram Soc. 2003;86(5):765–768. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916. 2003.tb03372.x
Ohta K. Magnetocrystalline Anisotropy and Magnetic Permeability of Mn-Zn-Fe Ferrites. J Phys Soc Japan. 1963;18(5):685–690. doi:10.1143/jpsj.18.685
Fischer R, Schrefl T, Kronmüller H, Fidler J. Grain-size dependence of remanence and coercive field of isotropic nanocrystalline composite permanent magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 1996;153(1–2):35–49. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(95)00494-7
Visser EG, Johnson MT. A novel interpretation of the complex permeability in polycrystalline ferrites. J Magn Magn Mater. 1991;101(1–3)143–147. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(91)90707-H
Goldman A. Handbook of modern ferromagnetic materials. Springer Science & Business Media; 2012. 649 p.
Otsuki E, Yamada S, Otsuka T, Shoji K, Sato T. Microstructure and physical properties of Mn-Zn ferrites for high-frequency power supplies. J Appl Phys. 1991;69(8):5942–5944. doi:10.1063/1.347822
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/chimtech.2023.10.3.16
Copyright (c) 2023 Ruslan Kuzmin, Roman Khabirov, Anna Mass, Elena Lozhkina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Chimica Techno Acta, 2014–2025
eISSN 2411-1414
Copyright Notice







