Evaluation of electrochemical performance of antimony modified screen-printed carbon electrodes
Abstract
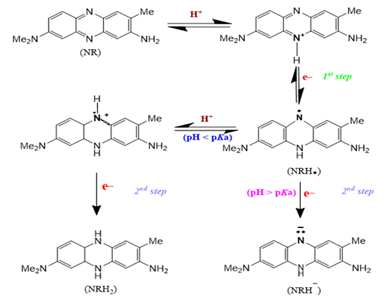
This study compares the electrochemical performance of screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs) modified with antimony (Sb/SPCEs) under different potentiostatic pre-plating conditions. Neutral Red (NR) was employed as a novel redox probe to evaluate the electrochemical performance of Sb/SPCEs. It was demonstrated that NR in the protonated form performs quasi-reversible redox transformations at bare SPCE and Sb/SPCEs in phosphate buffer solutions (pH 5.5±0.5) in the potential range of (−0.30)–(−0.75) V, where the antimony is not electroactive. Sb/SPCEs were studied electrochemically by cyclic voltammetry (CV) / electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and morphologically by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Cyclic voltammetry investigations revealed the dependence of the electrochemical performance of Sb/SPCEs on the degree of coverage of the substrate with the metal. The obtained CV, EIS, and SEM data are consistent. The lowest charge transfer resistance (Rct) value (6 Ω) was obtained at Sb/SPCE with the highest degree of antimony coverage. To investigate the electroanalytical performance of Sb/SPCEs, nickel (II) ions were utilized as a model analyte. A study of roughness factors and sensitivity towards nickel (II) ions for Sb/SPCEs using two-tailed Pearson's criterion revealed a high degree of correlation between their electrochemical and electroanalytical properties. The results show that using NR as a redox probe can help controlling modification processes during the development of innovative antimony-containing sensors.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Toghill KE, Wildgoose GG, Moshar A, Mulcahy C, Compton RG. Fabrication and characterization of a bismuth nanoparticle modified boron doped diamond electrode and its application to the simultaneous determination of cadmium(II) and lead(II). Electroanal. 2008;20:1731–1737. doi:10.1002/elan.200804277
Nguyen LD, Doan TCD, Huynh TM, Nguyen VNP, Dinh HH, Dang DMT, Dang CM. An electrochemical sensor based on polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan-thermally reduced graphene composite modified glassy carbon electrode for sensitive voltammetric detection of lead. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2021;345:130443. doi:10.1002/elan.200804277
Mardegan A, DalBorgo S, Scopece P, Moretto LM, Hočevar SB, Ugo P. Simultaneous adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetric determination of nickel(ii) and cobalt(ii) at an in situ bismuth-modified gold electrode. Electroanal. 2013;25:2471–2479. doi:10.1002/elan.201300320
Nigović B, Šimunić B, Hocevar S. Voltammetric measurements of aminosalicylate drugs using bismuth film electrode. Electrochim Acta. 2009;54:5678–5683. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.05.006
Jovanovski V, Hočevar SB, Ogorevc B. Ex situ prepared antimony film electrode for electrochemical stripping measurement of heavy metal ions. Electroanal. 2009;21:2321–2324. doi:10.1002/elan.200904692
Zhu WW, Li NB, Luo HQ. Simultaneous determination of chromium(III) and cadmium(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry on a stannum film electrode. Talanta. 2007;72:1733–1737. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2007.04.055
Economou A, Fielden PR. Mercury film electrodes: Developments, trends and potentialities for electroanalysis. Analyst. 2003;2:814–815. doi:10.1039/b201130c
Kokkinos C, Economou A. Stripping analysis at bismuth-based electrodes. Curr Anal Chem. 2008;4:183–190. doi:10.2174/157341108784911352
Serrano N, Díaz-Cruz JM, Ariño C, Esteban M. Antimony- based electrodes for analytical determinations. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem. 2016;77:203–213. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2016.01.011
Wang J, Lu J, Hocevar SB, Farias PAM, Ogorevc B. Bismuth-coated carbon electrodes for anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal Chem. 2000;72:3218–3222. doi:10.1021/ac000108x
Economou A. Screen-printed electrodes modified with “green” metals for electrochemical stripping analysis of toxic elements. Sensors. 2018;18:1032. doi:10.3390/s18041032
Bi Z, Chapman CS, Salaün P, Van Den Berg CMG. Determination of lead and cadmium in sea- and freshwater by anodic stripping voltammetry with a vibrating bismuth electrode. Electroanal. 2010;22:2897–2907. doi:10.1002/elan.201000429
Seifi A, Afkhami A, Madrakian T. Highly sensitive and simultaneous electrochemical determination of lead and cadmium ions by poly(thionine)/MWCNTs-modified glassy carbon electrode in the presence of bismuth ions. J Appl Electrochem. 2022;52:1513–1523. doi:10.1007/s10800-022-01728-4
Alves GMS, Magalhães JMCS, Soares HMVM. Simultaneous determination of nickel and cobalt using a solid bismuth vibrating electrode by adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry. Electroanal. 2013;25:1247–1255. doi:10.1002/elan.201200643
Hocevar SB, Švancara I, Ogorevc B, Vytřas K. Antimony film electrode for electrochemical stripping analysis. Anal Chem. 2007;79:8639–8643. doi:10.1021/ac070478m
Pérez-Ràfols C, Serrano N, Díaz-Cruz JM, Ariño C, Esteban M. New approaches to antimony film screen-printed electrodes using carbon-based nanomaterials substrates. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;916:17–23. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2016.03.003
Sebez B, Ogorevc B, Hocevar SB, Veber M. Functioning of antimony film electrode in acid media under cyclic and anodic stripping voltammetry conditions. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;785:43–49. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2013.04.051
Barceló C, Serrano N, Ariño C, Díaz-Cruz JM, Esteban M. Ex-situ antimony screen-printed carbon electrode for voltammetric determination of Ni(ii)-ions in wastewater. Electroanalysis. 2016;28:640–644. doi:10.1002/elan.201500511.
Tapia MA, Pérez-Ràfols C, Paštika J, Gusmão R, Serrano N, Sofer Z, Díaz-Cruz JM. Antimony nanomaterials modified screen-printed electrodes for the voltammetric determination of metal ions. Electrochim Acta. 2022;425. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2022.140690
Czop E, Economou A, Bobrowski A. A study of in situ plated tin-film electrodes for the determination of trace metals by means of square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochim Acta. 2011;56:2206–2212. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.12.017
Švancara I, Prior C, Hočevar SB, Wang J. A decade with bismuth-based electrodes in electroanalysis. Electroanal. 2010;22:1405–1420. doi:10.1002/elan.200970017
Rojas-Romo C, Aliaga ME, Arancibia V. Determination of molybdenum(VI) via adsorptive stripping voltammetry using an ex‒situ bismuth screen‒printed carbon electrode. Microchem J. 2020;154:104589. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2019.104589
Tapia MA, Pérez-Ràfols C, Oliveira FM, Gusmão R, Serrano N, Sofer Z, Díaz-Cruz JM. Antimonene-modified screen-printed carbon nanofibers electrode for enhanced electroanalytical response of metal ions. Chemosensors. 2023;11:219. doi:10.3390/chemosensors11040219
Ivoilova A, Malakhova N, Mozharovskaia P, Nikiforova A, Tumashov A, Kozitsina A, Ivanova A, Rusinov V. Study of different carbonaceous materials as modifiers of screen-printed carbon electrodes for the triazid as potential antiviral drug. Electroanal. 2022;34:1745–1755. doi:10.1002/elan.202100657
Christidi S, Chrysostomou A, Economou A, Kokkinos C, Fielden PR, Baldock SJ, Goddard NJ. Disposable injection molded conductive electrodes modified with antimony film for the electrochemical determination of trace Pb(II) and Cd(II). Sensors (Switzerland). 2019;19:4809. doi:10.3390/s19214809
Dal Borgo S, Jovanovski V, Hocevar SB. Antimony film electrode for stripping voltammetric measurement of Hg(II) in the presence of Cu(II). Electrochim Acta. 2013;88:713–717. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2012.10.122
Sopha H, Jovanovski V, Hocevar SB, Ogorevc B. In-situ plated antimony film electrode for adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetric measurement of trace nickel. Electrochem Commun. 2012;20:23–25. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2012.03.048
Sosa V, Barceló C, Serrano N, Ariño C, Díaz-Cruz JM, Esteban M. Antimony film screen-printed carbon electrode for stripping analysis of Cd(II), Pb(II), and Cu(II) in natural samples. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;855:34–40. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2014.12.011
Arancibia V, Nagles E, Rojas C, Gómez M. Ex situ prepared nafion-coated antimony film electrode for adsorptive stripping voltammetry of model metal ions in the presence of pyrogallol red. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2013;182:368–373. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2013.03.014
Kokkinos C, Economou A, Raptis I, Speliotis T. Novel disposable microfabricated antimony-film electrodes for adsorptive stripping analysis of trace Ni(II). Electrochem Commun. 2009;11:250–253. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2008.11.022
Pérez-Ràfols C, Trechera P, Serrano N, Díaz-Cruz JM, Ariño C, Esteban M. Determination of Pd(II) using an antimony film coated on a screen-printed electrode by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Talanta. 2017;167:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.084
Nigović B, Hocevar SB. Square-wave voltammetric determination of pantoprazole using exsitu plated antimony-film electrode. Electrochim Acta. 2013;109:818–822. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.173
Betancourth JM, Cuellar M, Ortiz PI, Pfaffen V. Multivariate cathodic square wave stripping voltammetry optimization for nitro group compounds determination using antimony film electrodes. Microchem J. 2018;139:139–149. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2018.02.028
Zhu WW, Li NB, Luo HQ. Simultaneous determination of chromium(III) and cadmium(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry on a stannum film electrode. Talanta. 2007;72:1733–1737. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2007.04.055
Tian YQ, Li NB, Luo HQ. Simultaneous determination of trace zinc(II) and cadmium(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry using a MWCNTs-NaDBS modified stannum film electrode. Electroanal. 2009;21:2584–2589. doi:10.1002/elan.200900249
Scholz F. Electroanalytical methods: guide to experiments and applications, 2nd Edition. Germany: Springer; 2010. 347 p. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-02915-8
Ortiz B, Saby C, Champagne GY, Bélanger D. Electrochemical modification of a carbon electrode using aromatic diazonium salts. 2. Electrochemistry of 4-nitrophenyl modified glassy carbon electrodes in aqueous media. J Electroanal Chem. 1998;455:75–81. doi:10.1016/S0022-0728(98)00252-69
Rooney MB, Coomber DC, Bond AM. Achievement of near-reversible behavior for the [Fe(CN)6]3–/4– redox couple using cyclic voltammetry at glassy carbon, gold, and platinum macrodisk electrodes in the absence of added supporting electrolyte. Anal Chem. 2000;72:3486–3491. doi:10.1021/ac991464m
Muna GW, Barrera E, Robinson L, Majeed H, Jones K, Damschroder A, Vila A. Electroanalytical performance of a Bismuth/Antimony composite glassy carbon electrode in detecting lead and cadmium. Electroanal. 2023;35:1–12. doi:10.1002/elan.202300019
Malakhova N, Kifle AB, Ivoilova A, Leonova N, Kozitsina A. Neutral red as a redox probe for comparative evaluation of electrochemical performance of bismuth modified electrodes. Anal Lett. 2024:1–18. doi:10.1080/00032719.2024.2314744
Nigoví B, Hocevar SB. Square-wave voltammetric determination of pantoprazole using ex situ plated antimony-film electrode. Electrochim Acta. 2013;109:818–822. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.173
Alves GMS, Rocha LS, Soares HMVM. Multi-element determination of metals and metalloids in waters and wastewaters, at trace concentration level, using electroanalytical stripping methods with environmentally friendly mercury free-electrodes: A review. Talanta. 2017;175:53–68. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2017.06.077
Nigović B, Hocevar SB. Antimony film electrode for direct cathodic measurement of sulfasalazine. Electrochim Acta. 2011;58:523–527. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2011.09.087
Walz JrFG, Terenna B, Rolince D. Equilibrium studies on neutral red–DNA binding. Biopolym Orig Res Biomol. 1975;14:825–837. doi:10.1002/bip.1975.360140411
Halliday CS, Matthews DB. Some electrochemical and photoelectrochemical properties of 3-Amino-7-dimethylamino-2-methylphenazine (Neutral Red) in aqueous solution. Austral J Chem. 1983;36:507–516. doi:10.1071/CH9830507c
Pauliukaite R, Ghica ME, Barsan M, Brett CMA. Characterisation of poly(neutral red) modified carbon film electrodes; Application as a redox mediator for biosensors. J Solid State Electrochem. 2007;11:899–908. doi:10.1007/s10008-007-0281-9
Jeykumari DRS, Narayanan SS. Covalent modification of multiwalled carbon nanotubes with neutral red for the fabrication of an amperometric hydrogen peroxide sensor. Nanotechnology. 2007;18: 125501. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/18/12/125501
Kaur B, Srivastava R. Simultaneous determination of epinephrine, paracetamol, and folic acid using transition metal ion-exchanged polyaniline-zeolite organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015;211:476–488. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.01.081
Hong J, Kim K. Neutral red and ferroin as reversible and rapid redox materials for redox flow batteries. ChemSusChem. 2018;11:1866–1872. doi:10.1002/cssc.201800303.
Li Z, Zhou Z, Yun G, Shi K, Lv X, Yang B. High-performance solid-state supercapacitors based on graphene-ZnO hybrid nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013;8:473. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-8-473
Ranjan B, Kaur D. Pseudocapacitive storage in molybdenum oxynitride nanostructures reactively sputtered on stainless-steel mesh towards an all-solid-state flexible supercapacitor. Small. 2023;2307723:1–17. doi:10.1002/smll.202307723
Stoynov ZB, Grafov BM, Savova-Stoynov BS, Elkin VV. Electrochemical Impedance. Moscow: Nauka; 1991. 336 p. Russian.
Finšgar M, Kovačec L. Copper-bismuth-film in situ electrodes for heavy metal detection. Microchem J. 2020;154:104635. doi:10.1016/j.microc.104635
Vladislavić N, Buzuk M, Brinić S, Buljac M, Bralić M. Morphological characterization of ex situ prepared bismuth film electrodes and their application in electroanalytical determination of the biomolecules. J Solid State Electrochem. 2016;20(8):2241–2250. doi:10.1007/s10008-016-3234-3
Yates F. Statistical tables for biological agricultural and medical research. London: Bookliver and Bookyd; 1938. 90 p.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/chimtech.2024.11.2.04
Copyright (c) 2024 Alexander B. Kifle, Nataliya Malakhova, Alexandra Ivoilova, Natalia Leonova, Svetlana Saraeva, Alisa Kozitsina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Chimica Techno Acta, 2014–2025
eISSN 2411-1414
Copyright Notice







