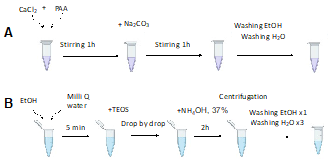
Inorganic nanocarriers based on calcium carbonate and silica oxide for passive breast cancer targeting
Abstract
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Zhou F, et al. Hyaluronan derivative decorated calcium carbonate nanoparticle as a potential platform for breast cancer synergistic therapy via blood coagulation and drug delivery. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023;83:104406. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104406
Huang H, et al. Smart responsive-calcium carbonate nanoparticles for dual-model cancer imaging and treatment. Ultrasonics. 2020;108:106198. doi:10.1016/j.ultras.2020.106198.
Barbezan AB, et al. Radioactive gold nanoparticles coated with BSA: A promising approach for prostate cancer treatment. Nanotheranostics. 2024;8(1):112–126. doi:10.7150/ntno.91507
Liang T, et al. Research progress of calcium carbonate nanomaterials in cancer therapy: challenge and opportunity. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1266888
Lin C, et al. Recent Developments in CaCO3 Nano-Drug Delivery Systems: Advancing Biomedicine in Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(2):275. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16020275
Li Y, et al. Calcium Carbonate/Polydopamine Composite Nanoplatform Based on TGF-β Blockade for Comfortable Cancer Immunotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(3):3187–3201. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c16571
Maleki Dizaj S, et al. Calcium carbonate nanoparticles as cancer drug delivery system. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015;12(10):1649–1660. doi:10.1517/17425247.2015.104953
Bahrom H, et al. Controllable Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate with Different Geometry: Comprehensive Analysis of Particle Formation, Cellular Uptake, and Biocompatibility. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7(23):19142–19156. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05128
Kim TG, et al. Synthesis of Size Controlled Spherical Silica Nanoparticles via Sol-Gel Process within Hydrophilic Solvent. J Kor Ceram Soc. 2017;54(1):49–54. doi:10.4191/kcers.2017.54.1.10
Wu S-H, Mou C-Y, Lin H-P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42(9):3862. doi:10.1039/c3cs35405a
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1968;26(1):62–69. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(68)90272-5
Bhatt N, et al. Preparation of Silica Nano-Particles by Sol-Gel Method and Its Characterization. J Graphic Era Univer. 2021. doi:10.13052/jgeu0975-1416.927
Hanafy NAN, El-Kemary M, Leporatti S. Reduction diameter of CaCO3 crystals by using poly acrylic acid might improve cellular uptake of encapsulated curcumin in breast cancer. J Nanomed Res. 2018;7:235-239. https://medcraveonline.com/JNMR/JNMR-07-00193.pdf
Zhou X, et al. Single-injection subunit vaccine for rabies prevention using lentinan as adjuvant. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;254:128118. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128118
Moore CJ, et al. Controlling colloidal stability of silica nanoparticles during bioconjugation reactions with proteins and improving their longer-term stability, handling and storage. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(10):2043–2055. doi:10.1039/C4TB01915F
Karpov T, et al. Universal Chelator-Free Radiolabeling of Organic and Inorganic-Based Nanocarriers with Diagnostic and Therapeutic Isotopes for Internal Radiotherapy. Chem Mater. 2022;34, № 14:6593–6605. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c01507
Abrishami A, et al. Hybridized quantum dot, silica, and gold nanoparticles for targeted chemo-radiotherapy in colorectal cancer theranostics. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):393. doi:10.1038/s42003-024-06043-6
Rabanel MJ, et al. Drug-Loaded Nanocarriers: Passive Targeting and Crossing of Biological Barriers. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(19):3070–3102. doi:10.2174/092986712800784702
Shekunov BY, et al. Particle Size Analysis in Pharmaceutics: Principles, Methods and Applications. Pharm Res. 2007;24(2):203–227. doi:10.1007/s11095-006-9146-7
Titus D, James Jebaseelan Samuel E, Roopan SM. Nanoparticle characterization techniques. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Nanoparticles. Elsevier, 2019:303–319. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-102579-6.00012-5
Muslimov AR, et al. An investigation of calcium carbonate core-shell particles for incorporation of 225Ac and sequester of daughter radionuclides: in vitro and in vivo studies. Journal of Controlled Release. 2021;330:726–737. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.01.008
Mahmed N, et al. Synthesis of Nanosized Silica and Silver-Doped Silica Nanoparticles for Heat Transfer Fluids Applications. Key Eng Mater. 2015;660:155–160. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.660.155
Karpov TE, et al. Impact of metallic coating on the retention of 225Ac and its daugthers within core–shell nanocarriers. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;608:2571–2583. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.187
Timin AS, et al. Triple-responsive inorganic–organic hybrid microcapsules as a biocompatible smart platform for the delivery of small molecules. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(45):7270–7282. doi:10.1039/C6TB02289H
Tabatabaei S, et al. Experimental study of the synthesis and characterisation of silica nanoparticles via the sol-gel method. J Phys Conf Ser. 2006;26:371–374. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/26/1/090
Nazarabady MM, Farzi G. Morphology control to design p(acrylic acid)/silica nanohybrids with controlled mechanical properties. Polymer (Guildf). 2018;143:289–297. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2018.02.026
Wilhelm S, et al. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;1(5):16014. doi:10.1038/natrevmats.2016.14
Hanafi-Bojd MY, et al. Surface functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an effective carrier for epirubicin delivery to cancer cells. Eur J Pharmac Biopharmac. 2015;89:248–258. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.12.009
Chang J, et al. A pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based drug delivery system for targeted breast cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(17):3375–3385. doi:10.1039/D1TB02828F
Som A, et al. Calcium carbonate nanoparticles stimulate tumor metabolic reprogramming and modulate tumor metastasis. Nanomedicine. 2019;14(2):169–182. doi:10.2217/nnm-2018-0302
Dubey RS, Rajesh YBRD, More MA. Synthesis and Characterization of SiO2 Nanoparticles via Sol-gel Method for Industrial Applications. Mater Today Proc. 2015;2(4–5):3575–3579. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.098
Barhoum A, et al. Preparation and characterization of ultra-hydrophobic calcium carbonate nanoparticles. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. 2014;64:012037. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/64/1/012037
Tsoi KM, et al. Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver. Nat Mater. 2016;15(11):1212–1221. doi:10.1038/nmat4718
Soo Choi H, et al. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(10):1165–1170. doi:10.1038/nbt1340
Bahcecioglu G, et al. Breast cancer models: Engineering the tumor microenvironment. Acta Biomater. 2020;106:1–21. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.006
Wagenblast E, et al. A model of breast cancer heterogeneity reveals vascular mimicry as a driver of metastasis. Nat. 2015;520(7547):358–362. doi:10.1038/nature14403
Ejigah V, et al. Approaches to Improve Macromolecule and Nanoparticle Accumulation in the Tumor Microenvironment by the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(13):2601. doi:10.3390/polym14132601
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/chimtech.2024.11.2.12
Copyright (c) 2024 Alisa S. Postovalova, Yulia A. Tishchenko, Vladislava A. Rusakova, Timofey E. Karpov, Nina V. Gavrilova, Anna S. Rogova, Irina A. Gorbunova, Alexander S. Timin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Chimica Techno Acta, 2014–2025
eISSN 2411-1414
Copyright Notice







