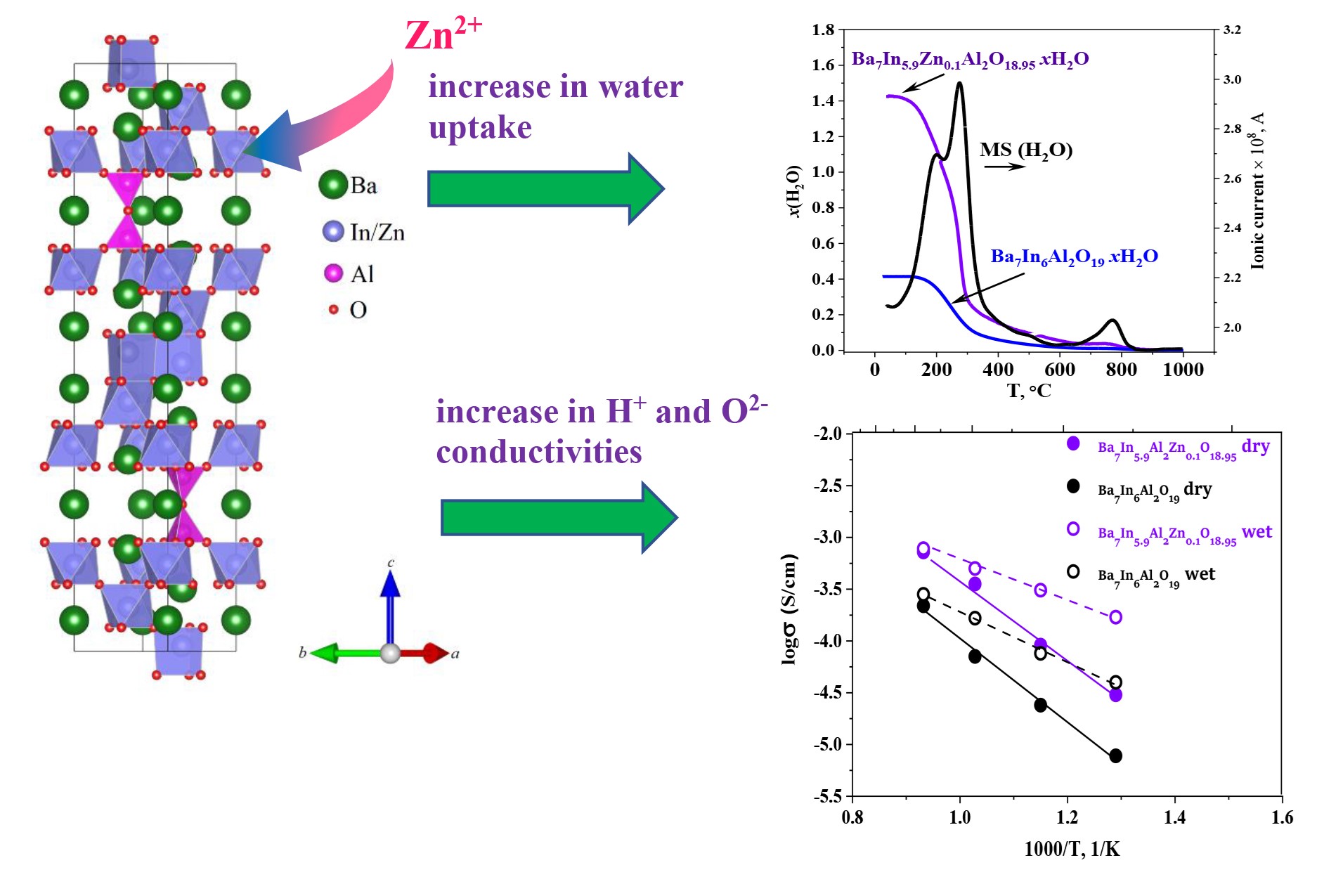
The novel Zn-doped hexagonal perovskite Ba7In6Al2O19: electrical conductivity and hydration
Abstract
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Takahashi T, Iwahara H. Solid state ionics: proton conduction in perovskite type solid solutions. Rev Chim Miner. 1980;17(4):243–253. doi:10.1002/chin.198114014
Iwahara H, Esaka T, Uchida H, Maeda N. Proton conduction in sintered oxides and its application to steam electrolysis for hydrogen production. Solid State Ionics. 1981;3–4:359–363. doi:10.1016/0167-2738(81)90113-2
Karuppiah K, Ashok A. Review on Proton and Oxide Ion Conducting Perovskite Materials for SOFC Applications. Nanomater Energy. 2019;8(1):1–8. doi:10.1680/jnaen.18.00004
Medvedev D, Murashkina A, Pikalova E, Demin A, Podias A, Tsiakaras P. BaCeO3: Materials development, properties and application. Prog Mater Sci. 2014;60:72–129. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.08.001
Tayyab M, Rauf S, Khan AZ, Tayyab Z, Khan K, Hussain I, Hussain MB, Waseem M, Alodhayb AN, Fu XZ, Qasim M, Tian Y. Breaking barriers: Novel approaches to proton-conducting oxide materials. Ceram Int. 2024. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.06.008
Scholten MJ, Schoonman J, van Miltenburg JC, Oonk HAJ. Synthesis of strontium and barium cerate and their reaction with carbon dioxide. Solid State Ionics. 1993;61:83–91. doi:10.1016/0167-2738(93)90338-4
Ma G, Shimura T, Iwahara H. Ionic conduction and nonstoichiometry in BaxCe0.90Y0.10 O3-α. Solid State Ionics. 1998;110:103–110. doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(98)00130-1
Ryu KH, Haile SM. Chemical stability and proton conductivity of doped BaCeO3 –BaZrO3 solid solutions. Solid State Ionics. 1999;125:355–367. doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00196-4
Radojkovic A, Zunic M, Savic SM, Brankovic G, Brankovic Z. Chemical stability and electrical properties of Nb doped BaCe0.9Y0.1O3-δ as a high temperature proton conducting electrolyte for IT-SOFC. Ceram Int. 2013;39(1):307–313. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.06.026
Kannan R, Singh K, Gill S, Furstenhaupt T, Thangadurai V. Chemically Stable Proton Conducting Doped BaCeO3 - No More Fear to SOFC Wastes. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1–5. doi:10.1038/srep02138
Medvedev DA, Lyagaeva JG, Gorbova EV, Demin AK, Tsiakaras P. Advanced materials for SOFC application: Strategies for the development of highly conductive and stable solid oxide proton electrolytes. Prog Mater Sci. 2016;75:38–79. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.08.001
Medvedev D, Lyagaeva J. Plaksin S, Demin A, Tsiakaras P. Sulfur and carbon tolerance of BaCeO3-BaZrO3 proton-conducting materials. J Power Sources. 2015;273:716–723. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.09.116
Sazinas R, Bernuy-Lopez C, Einarsrud M-A. Grande T. Effect of CO2 exposure on the chemical stability and mechanical properties of BaZrO3-ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc. 2016;99:3685–3695. doi:10.1111/jace.14395
Lacz A, Silarska K, Piecha I, Pasierb P. Structure, chemical stability and electrical properties of BaCe0.9Y0.1O3-δ proton conductors impregnated with Ba3(PO4)2. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2016;41:13726–13735. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.06.009
Somekawa T, Matsuzaki Y, Sugahara M, Tachikawa Y, Matsumoto H, Taniguchi S, Sasaki K. Physicochemical properties of Ba(Zr,Ce)O3-δ-based proton-conducting electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells in terms of chemical stability and electrochemical performance. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2017;42(26):16722–16730. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.04.26
Stavrakakis E, West M, Johnston S, McIllwaine R, Poulidi D. Hydration, CO2 stability and wireless electrochemical promotion studies on yttria-doped Ba(Ce,Zr)O3 perovskites. Ionics. 2019;25:1243–1257. doi:10.1007/s11581-019-02836-6
Guo H, Li Y, Jiang L, Sha Y, Guoa S, Han D. Transport properties of the Ba(Zr,Ce,Y,Yb)O3−δ proton conductor: the real role of co-substitution of Y and Yb. J Mater Chem A. 2024;12:5875–5884. doi:10.1039/D3TA07486B
Saito K, Umeda K, Fujii K, Mori K, Yashima M. High Proton Conduction by Full Hydration in Highly Oxygen Deficient Perovskite. J Mater Chem A. 2024;12(22):13310–13319. doi:10.1039/D4TA01978D
Yang X, Fernandez-Carrión AJ, Geng X, Kuang X. B-Site Deficient Hexagonal Perovskites: Structural Stability, Ionic Order-Disorder and Electrical Properties. Prog Solid State Chem. 2024;74:1-19. doi:10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2024.100459
Fop S, McCombie KS, Wildman EJ, Skakle JMS, Irvine JTS, Connor PA, et al. High oxide ion and proton conductivity in a disordered hexagonal perovskite. Nat Mater. 2020;19:752–775. doi:10.1038/s41563-020-0629-4
Fop S, McCombie KS, Wildman EJ, Skakle JMS, McLaughlin AC. Hexagonal perovskite derivatives: a new direction in the design of oxide ion conducting materials. Chem Commun. 2019;55:2127–2137. doi:10.1039/C8CC09534E
Fop S. Solid oxide proton conductors beyond perovskites. J Mater Chem A. 2021;9:18836–18856. doi:10.1039/d1ta03499e
Tarasova NA, Animitsa IE, Galisheva AO, Medvedev DA. Layered and Hexagonal Perovskites as Novel Classes of Proton-Conducting Solid Electrolytes. A Focus Review. Electrochem Mater Technol. 2022;1:20221004. doi:10.15826/elmattech.2022.1.004
Murakami T, Hester J, Yashima M. High Proton Conductivity in Ba5Er2Al2ZrO13, a Hexagonal Perovskite-Related Oxide with Intrinsically Oxygen-Deficient Layers. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142:11653–11657. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c02403
Matsuzaki K, Saito K, Ikeda Y, Nambu Y, Yashima M. High Proton Conduction in the Octahedral Layers of Fully Hydrated Hexagonal Perovskite-Related Oxides. J Am Chem Soc. 2024;146:18544–18555. doi:10.1021/jacs.4c04325
Andreev R, Korona D, Anokhina I, Animitsa I. Proton and oxygen-ion conductivities of hexagonal perovskite Ba5In2Al2ZrO13. Mater. 2022;15(11):1–18. doi:10.3390/ma15113944
Andreev RD, Korona DV, Anokhina IA, Gilev AR, Animitsa IE. Transport properties of In3+- and Y3+-doped hexagonal perovskite Ba5In2Al2ZrO13. Russ J Electrochem. 2023;(59):190–203. doi:10.1134/S1023193523030035
Andreev RD, Animitsa IE Protonic transport in the novel complex oxide Ba5Y0.5In1.5Al2ZrO13. Ionics. 2023;29(11):4647–4658. doi:10.1007/s11581-023-05187-5
Andreev RD, Korona DV, Vlasov MI, Animitsa IE. Protonic ceramics Ba5In2–xYxAl2ZrO13 with the perovskite-related hexagonal structure for solid oxide fuel cells: synthesis, optical band gap and transport properties. Ceram Int. 2024. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.04.227
Suzuki Y, Murakami T, Fujii K, Hester JR, Yasui Y, Yashima M. Simultaneous reduction of proton conductivity and enhancement of oxide-ion conductivity by aliovalent doping in Ba7Nb4MoO20. Inorg Chem 2022;61:7537–7545. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c00671
Sakuda Y, Hester JR, Yashima M. Improved oxide-ion and lower proton conduction of hexagonal perovskite-related oxides based on Ba7Nb4MoO20 by Cr6+ doping. J Ceram Soc Jpn. 2022;130:442–447. doi:10.2109/jcersj2.21192
Shpanchenko RV, Abakumov AM, Antipov EV, Nistor, Tendeloo G, Amelinckx SJ. Structural study of the new complex oxides Ba5-ySryR2-xAl2Zr1+xO13+x/2 (R = Gd-Lu, Y, Sc). Solid State Chem. 1995;118:180–192. doi:10.1006/jssc.1995.1329
Shpanchenko RV, Nistor L, Tendeloo G, Amelinckx S, Antipov EV, Kovba LM. High–resolution electron microscopic study of Ba7Sc6Al2O19 and related phases. J Solid State Chem. 1994;113:193–204. doi:10.1006/jssc.1994.1359
Andreev R, Animitsa I. Transport properties of intergrowth structures Ba5In2Al2ZrO13 and Ba7In6Al2O19. Appl Sci. 2023;13(6):1–14. doi:10.3390/app13063978
Zirconia Project. Available online: https://zirconiaproject.wordpress.com/devices/zirconiam/
Shannon RD. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. 1976; A32:751–767. doi:10.1107/S0567739476001551
Tarasova N, Animitsa I, Galisheva A, Korona D. Incorporation and Conduction of Protons in Ca, Sr, Ba-Doped BaLaInO4 with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure. Mater. 2019;12(10):1–14. doi:10.3390/ma12101668
Troncoso L, Alonso JA, Fernández-Díaz MT, Aguadero A. Introduction of interstitial oxygen atoms in the layered perovskite LaSrIn1-xBxO4+δ system (B=Zr, Ti). Solid State Ionics. 2015;282:82–87. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2015.09.014
Aguadero A, Alonso JA, Martínez-Lope MJ, Fernández-Díaz MT, Escudero MJ, Daza L. In situ high temperature neutron powder diffraction study of oxygen-rich La2NiO4+δ in air: correlation with the electrical behaviour. J Mater Chem. 2006;16:3402–3408. doi:10.1039/b605886h
Shpanchenko RV, Antipov EV, Paromova MV, Kovba LM. Crystal structure of Ba7Sc6Al2O19. Zhurnal Neorganicheskoi Khimii. 1991;136:1402–1407.
Unti LF Kultz, Grzebielucka EC, Chinelatto ASA, MatherGC, Chinelatto AL. Synthesis and electrical characterization of Ba5Nb4O15 and Ba5Nb3.9M0.1O(15-δ) (M = Ti, Zr) hexagonal perovskites. Ceram Int. 2019;45;5087–5092. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.11.211
McCombie KS, Wildman EJ, Fop S, Smith RI,. Skakle JMS, Mclaughlin AC. The Crystal Structure and Electrical Properties of the Oxide Ion Conductor Ba3WNbO8.5. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6;5290–5295. doi:10.1039/C7TA08989A
Frade JR. Theoretical behavior of concentration cells based on ABO3 perovskite materials with protonic and oxygen-ion conduction. Solid State Ionics. 1995;78:87–97. doi:10.1016/0167-2738(95)00008-T
Baek HD. Modeling of electrical conductivity in high-temperature proton-conducting oxides. Solid State Ionics. 1998;110:255–262. doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(98)00138-6
Glöckner R, Neiman A, Larring Y, Norby T. Protons in Sr3(Sr1+xNb2−x)O9−3x/2 perovskite. Solid State Ionics. 1999;125:369–376. doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00197-6
Sakuda Y, Murakami T, Avdeev M, Fujii K, Yasui Y, Hester JR, et al. Dimer-mediated cooperative mechanism of ultrafast-ion conduction in hexagonal perovskite-related oxides. Chem Mater. 2023;35:9774–9788. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c02378
Tarasova N, Galisheva A, Animitsa I, Korona D, Davletbaev K. Novel proton-conducting layered perovskite based on BaLaInO4 with two different cations in B-sublattice: Synthesis, hydration, ionic (O2−, H+) conductivity. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2022;47:18972–18982. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.04.112
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/chimtech.2024.11.4.03
Copyright (c) 2024 Irina Animitsa, Daniil Korona, Arina Bushueva, Roman Andreev, Sergey Nokhrin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
© Website Chimica Techno Acta, 2014–2024
ISSN 2411-1414 (Online)
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International







