ПРИМЕНЕНИЕ ВНУТРЕННЕГО СТАНДАРТА ПРИ ИЗОТОПНОМ АНАЛИЗЕ ВЫСОКООБОГАЩЕННОГО “КРЕМНИЯ-28” МЕТОДОМ МАСС-СПЕКТРОМЕТРИИ ВЫСОКОГО РАЗРЕШЕНИЯ С ИНДУКТИВНО СВЯЗАННОЙ ПЛАЗМОЙ
Аннотация
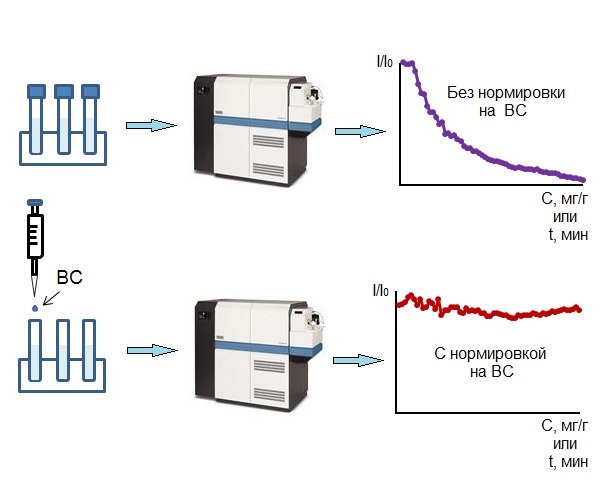
Для изучения изотопических эффектов в полупроводниковых материалах требуются монокристаллы с высокой химической и изотопной чистотой. Надежность полученных данных о величине и направлении изотопических сдвигов зависит от точности определения концентрации всех стабильных изотопов. При изотопном анализе обогащенного “кремния-28” с высокой степенью обогащения (более 99.99 %) необходимо определять примеси изотопов 29Si и 30Si на уровне 10-3 ¸ 10-5 ат. %. На таком уровне концентраций указанные изотопы можно рассматривать как примеси. Достижение высокой точности измерений при одновременной регистрации основного и “примесных” изотопов в таком широком интервале концентраций затруднительно. Регистрацию аналитических сигналов изотопов кремния приходится проводить на растворах с разной концентрацией матрицы. Использование растворов с высокой концентрацией матричного элемента требует введения поправок на матричные помехи и дрейф чувствительности прибора в процессе измерения. Снизить влияние необратимых неспектральных помех и дрейфа чувствительности можно при использовании метода внутренней стандартизации. Противоречивость литературных данных о критериях выбора внутреннего стандарта потребовала исследования поведения сигналов элементов “кандидатов во внутренний стандарт“ для одноколлекторного масс-спектрометра высокого разрешения с индуктивно связанной плазмой ELEMENT 2 от концентрации матричного элемента и природы растворителя, а также от времени распыления раствора. Учет необратимых неспектральных матричных помех и аппаратного дрейфа при изотопном анализе обогащенного “кремния-28” и исходного 28SiF4 методом масс-спектрометрии с индуктивно связанной плазмой позволил снизить в 3-5 раз случайную составляющую и более чем на порядок систематическую составляющую погрешности измерения по сравнению с методом внешнего стандарта. Это позволило проводить с достаточной точностью оперативный контроль изотопного состава обогащенного “кремния-28”, как в виде тетрафторида кремния, так и получаемого из него поликристаллического кремния с помощью одного серийного прибора в интервале изотопных концентраций 0.0001–99.999 ат. %.
Ключевые слова: масс-спектрометрия высокого разрешения с индуктивно связанной плазмой, изотопный анализ, изотопнообогащенный кремний, внутренний стандарт
Полный текст:
PDF (Russian)Литература
REFERENCES
Berglund M., Wieser M.E. Isotopic compositions of the elements 2009. Pure Appl. Chem., 2011, vol. 83, no 2, pp. 397-410. doi:10.1351/PAC-REP-10-06-02.
Plotnichenko V. G., Nazaryants V. O., Kryukova E. B., Koltashev V. V., Sokolov V. O., Gusev A. V., Gavva V. A., Kotereva T. V., Churbanov M. F. and Dianov E. M. Refractive index spectral dependence, Raman spectra,and transmission spectra of high-purity 28Si, 29Si, 30Si, and natSi single crystals. Appl. Opt., 2011, vol. 50, no 23, pp. 4633-4641. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.004633.
Inyushkin A.V., Taldenkov A.N., Gusev A.V., Gibin A.M. , Gavva V.A., Kozyrev E.A. Thermal conductivity of single-crystal monoisotopic 29Si in the temperature range 2.4-410 K. Physics of the Solid State, 2013, vol. 55, no 1, pp. 235-239. doi: 10.1134/S1063783413010150
Detochenko A.P., Denisov S.A., Mashin A.I., Bulanov A.D., Nezhdanov A.V., Ezhevskii A.A., Stepikhova M.V., Chalkov V.Y., Trushin V.N., Shengurov D.V., Shengurov V.G., Gavva V.A., Drozdov M.N., Abrosimov N.V., Riemann H. Epitaxially Grown monoisotopic Si, Ge, and Si1–XGeX alloy layers: production and some properties. Semiconductors, 2016, vol. 50, no 3, pp. 345-348. doi: 10.1134/S1063782616030064.
Moutanabbir O., Senz S., Zhang Zh., Gösele U. Synthesis of isotopically controlled metal-catalyzed silicon nanowires. Nano Today, 2009, vol. 4, pp. 393-398. doi:10.1016/J.NANTOD.2009.08.009.
De Bièvre P., Valkiers S., Taylor P.D.P. The importance of the Avogadro constant for amount-of-substance measurements. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem., 1998, vol., 361, no 3, pp. 227-234. doi: 10.1007/s002160050870.
Becker P., Friedrich H., Fujii K., Giardini W., Mana G., Picard A., Pohl H-J., Riemann H. and Valkiers S. The Avogadro constant determination via enriched silicon-28. Meas. Sci. Technol., 2009, vol. 20, no 9, pp. 092002. doi: 10.1088/0957 0233/20/9/092002
Devyatykh G.G., Bulanov A.D., Gusev A.V., Kovalev I.D., Krylov V.A., Potapov A.M., Sennikov P.G., Adamchik S.A., Gavva V A.A., Kotkov A.P., Churbanov M.F., Dianov E.M., Kaliteevsky A.K., Godisov O.N., Paul H.-Y., Becker P., Riemann H., Abrosimov N.V. Vysokochistyy monokristallicheskiy monoizotopnyy kremniy−28 dlya utochneniya chisla Avogadro [High-purity monocrystalline monoisotopic silicon-28 to refine the Avogadro number ]. Doklady Akademii nauk [Reports of the Academy of Sciences], 2008, vol. 42, no 1, pp. 61-64. (in Russian).
Georg R.B., Reynolds B.C., Frank M., Halliday A.N. New sample preparation techniques for the determination of Si isotopic compositions using MC-ICPMS. Chem. Geol., 2006, vol. 235, pp. 95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.06.006.
Basile-Doelsch I., Meunier J. D. and Parron C. Another continental pool in the terrestrial silicon cycle. Nature., 2005, vol. 433, pp.399–402. doi: 10.1038/nature03217.
Opfergelt S., Delmelle P. Silicon isotopes and continental weathering processes: Assessing controls on Si transfer to the ocean. C. R. Geoscience, 2012, vol. 344, pp. 723-738. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2012.09.006.
Sermyagin B.A., Pupyshev A.A. [Some questions of the estimation of errors of mass spectrometric measurements of the isotopic composition of elements]. Mass-spektrometriya [Mass spectrometry], 2008, vol. 5, no 3, pp. 163-184. (in Russian).
Rienitz O., Pramann A., and Schiel D. Novel concept for the mass spectrometric determination of absolute isotopic abundances with improved measurement uncertainty: Part I. - theoretical derivation and feasibility study. Int. J. Mass Spectrom., 2010, vol. 289, pp. 47-53. doi:10.1016/J.IJMS.2009.09.010.
Karandashev V.K., Leikin A.Yu., Zhernokleeva K.V. Reduction of matrix effects in ICP-MS by optimizing settings of ion optics. Journal of Analytical Chemistry. 2014, vol. 69, no 1, pp. 22 - 30. doi: 10.1134/S1061934814010092.
Agatemor C., Beauchemin D. Matrix effects in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: A review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2011, vol. 706, pp. 66-83. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.08.027.
Dams R.F.J., Goossens J., Moens L. Spectral and non-spectral interferences in inductively coupled plasma mass-spectrometry. Mikrochim. Acta, 1995, vol. 119, no 3–4, pp. 277–286. doi: 10.1007/BF01244007.
Thompson J.J., Houk R.S. A study of internal standardization in inductively coupled plasma – mass spectrometry. Appl. Spectrosc., 1987, vol. 41, no 5, pp. 801-806. doi:10.1366/0003702874448265
Vanhaecke F., Vanhoe H., Dams R. The use of internal standards in ICP-MS. Talanta, 1992, vol. 39, no 7, pp. 737-742. doi: 10.1016/0039-9140(92)80088-u.
Osipov K.B., Seregina I.F., Bolshov M.A. [Elimination of matrix non-spectral interference in the elemental analysis of biological fluids on a quadrupole mass spectrometer with inductively coupled plasma]. Analitika i kontrol' [Analytics and Control], 2014, vol.18. no 2, pp.150-163. (in Russian).
Sartoros Ch., Salin E.D. Automatic selection of internal standards in inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B, 1999, vol. 54, no 11, pp. 1557–1571. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(99)00089-0
Finley-Jones H. J., Molloy J. L. and Holcombe J. A. Choosing Internal Standards Based on a Multivariate Analysis Approach with ICP(TOF)MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2008, vol. 23, pp. 1214-1222. doi: 10.1039/b804048f.
Dauphas N., Pourmand A., Teng F.-Z. Routine isotopic analysis of iron by HR-MC-ICPMS: How precise and how accurate? Chem. Geol., 2009, vol.267, pp. 175-184. doi:10.1016/J.CHEMGEO.2008.12.011.
Doherty W., Lightfoot P.C., Ames D.E. A drift correction optimization technique for the reduction of the inter-measurement dispersion of isotope ratios measured using a multi-collector plasma mass spectrometer. Spectrochimica Acta. Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2014, vol.98, pp. 28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2014.05.008.
Rodushkin I, Ruth T., Klockare D. Non-spectral interferences caused by a saline water matrix in quadrupole and high resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1998, vol. 13, pp. 159-166. doi: 10.1039/a706069f.
Otopkova P. A., Potapov A. M., Suchkov A. I., Bulanov A. D., Lashkov A. Yu., Kurganova A. E. Isotopic analysis of highly enriched crystalline 28Si and initial 28SiF4 by high-resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, vol. 74, no 13, pp. 1341-1346. doi: 10.1134/S1061934819130100.
Kovalev I.D., Potapov A.M., Bulanov A.D. [Measurement of the isotopic composition of isotopically enriched silicon and its volatile compounds by laser mass spectrometry]. Mass-spektrometriya [Mass spectrometry], 2004, vol. 1, no 1, pp. 37-44. (in Russian).
Pramann A., Rienitz O., Schiel D., Güttler B. and Valkiers S. Novel concept for the mass spectrometric determination of absolute isotopic abundances with improved measurement uncertainty: Part 3 - Molar mass of silicon highly enriched in 28Si. Int. J. Mass Spectrom., 2011. vol. 305, no 1, pp. 58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2011.05.017.
Yang L., Mester Z., Sturgeon R.E. and Mejia J. Determination of the atomic weight of 28Si-enriched silicon for a revised estimate of the Avogadro constant. Anal. Chem., 2012, vol.84, pp. 2321-2327. doi: 10.1021/ac203006j.
Vocke Jr.R.D., Rabb S.A. and Turk G.C. Absolute silicon molar mass measurements, the Avogadro constant and the redefinition of the kilogram. Metrologia, 2014, vol. 51, pp. 361-375. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/51/5/361.
Pramann A, Lee K.-S., Noordmann J, Rienitz O. Probing the homogeneity of the isotopic composition and molar mass of the “Avogadro“-crystal. Metrologia, 2015, vol. 52, pp. 800-810. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/52/6/800.
Efimov A.I., Belorukova L.P., Vasilkova I.V., Chechev V.P. Svoystva neorganicheskikh soyedineniy. Spravochnik [Properties of inorganic compounds. Reference book]. Leningrad, Chemistry, 1983. 392 p. (in Russian).
Beard B.L., Johnson C.M., Skulan J.L., Nealson K.H., Cox L., Sun H. Application of Fe isotopes to tracing the geochemical and biological cycling of Fe. Chem. Geol., 2003, vol. 195, pp. 87-117. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00390-X.
Tangen A., Lund W. A multivariate study of the acid effect and the selection of internal standards for inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B, 1999, vol. 54, pp. 1831-1838. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(99)00126-3.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/analitika.2021.25.2.009
Ссылки
- На текущий момент ссылки отсутствуют.
