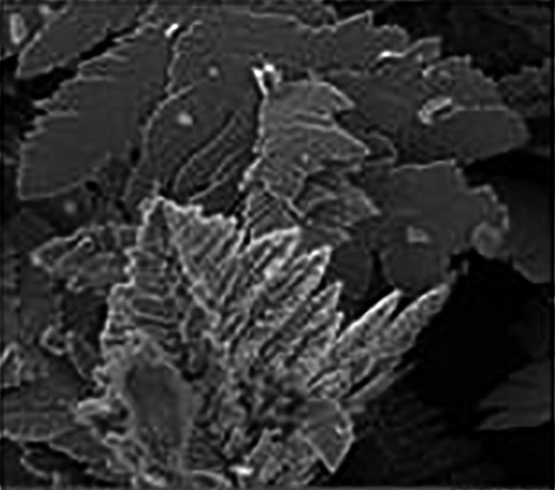
Dynamics of electrocrystallization of dendritic zinc deposits in galvanostatic and potentiostatic modes
Abstract
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Neikov O, Naboychenko S. Handbook of non-ferrous metal powders: Technologies and applications. Naboychenko S, Mourachova I, Gopienko V, Frishberg I, Lotsko D, editors. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2009. 634 p. ISBN: 978-1-85617-422-0.
Patrushev AV, Ostanina TN, Rudoy VM. Electrochemical methods for the determination of surface area of dendritic deposits. In: Proceedings of Phisycal chemistry and electrochemistry of molten and solid electrolytes. XVI Russian conference; 2013; Ekaterinburg, Russia. Russian.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15826/chimtech.2015.2.3.022
Copyright (c) 2015 V. S. Nikitin, T. N. Ostanina, V. M. Rudoi, A. S. Farlenkov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
© Chimica Techno Acta, 2014–2024
ISSN 2411-1414 (Online)
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International






